| Airway remodelling is long-term damage to the lungs caused by repeated or severe asthma flare-ups. It involves thickening of the airway walls, damage to the airway lining, and increased mucus production, all of which make breathing harder and reduce lung function. These changes can build up over time. Risk factors include frequent or severe flare-ups, long-term asthma, smoking, and exposure to irritants. Good asthma control helps prevent airway remodelling by reducing inflammation and protecting lung function. Daily preventer medicine, avoiding triggers, staying vaccinated, and regular check-ups are key to reducing this risk. |
What Is Airway Remodelling and How It Damages the Lungs in Asthma
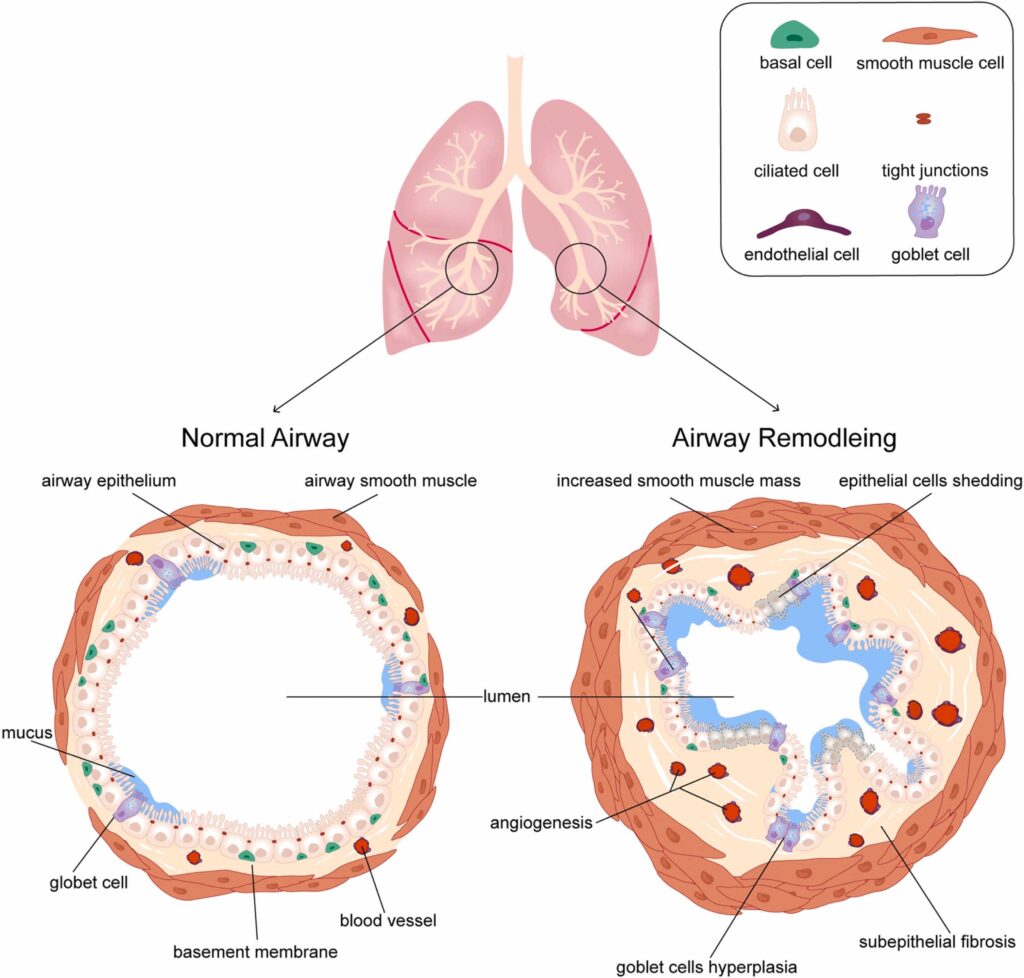
When people with asthma have a flare-up, it is more difficult to breathe because of the narrowing of the airways. This narrowing can occur because of contraction of the muscle around the air tubes, inflammation in the airway wall, or both of these processes.
It is important to realise that after an episode of asthma the lungs often don’t quite go back to normal. Over time damage accumulates and changes the structure of the airways: this is Airway Remodelling.
People with asthma are often not aware of these changes in their lungs until they are quite advanced and begin to affect everyday activities.
What changes occur?
- Thickening of airway walls: The muscles around the airways get bigger and thicker the more they contract. Inflammation also thickens the airway lining over time. This tends to result in permanent narrowing of the airways, making breathing increasingly difficult over many years.
- Damaged airway lining: the lining of the airway which normally acts as a protective barrier and a crucial part of your immune defence becomes damaged from inflammation. The hairlike structures that help remove debris from the airways are also damaged.
- Increased mucous production: gland enlargement in the airway walls causes excess mucous production, which can no longer be cleared as effectively. This contributes to airway blockage.
These changes lead to reduced lung function, more frequent infections and more frequent asthma flare-ups.
The risk of airway remodelling increases with:
- Frequency of flare ups
- Severity of flare ups
- Duration of asthma in years
- Smoking and other noxious exposures
Having even one severe asthma attack a year can lead to a decline in lung function, similar to damage caused by smoking.
What happens during an asthma attack?
Remodelling means that the changes that occur during an asthma flare-up, become more permanent.
Why is good asthma control important?
Maintaining good asthma control with daily self-management will help reduce the risk of airway remodelling by:
- Reducing airway inflammation
- Reducing airway muscle tightening
- Protecting lung function
- Preventing flare-ups
Key tips for managing asthma and reducing risk of airway remodelling
- Take preventer medicine as prescribed to reduce inflammation and asthma symptoms.
- Avoid exposure to triggers such as infections, allergens and irritants where possible.
- Make sure your vaccinations are up to date to reduce the impact of respiratory infections.
- Schedule regular reviews with your healthcare provider to check your lung function and treatment plan.
- Avoid smoking or vaping, as both irritate the airways and increases the risk of airway remodelling.
References
- AbuJabal, R. et al. (2024) ‘Role of IL-5 in asthma and airway remodelling’, Clinical and Experimental Allergy, 54(8).
- Bergeron, C., Tulic, M. and Hamid, Q. (2010) ‘Airway Remodelling in Asthma: From Benchside to Clinical Practice’, Canadian Respiratory Journal, 17(4), pp. e85-e93. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2933777/
- Chanaz, P.C. & Varricchi, G. (2024) ‘The airway epithelium plays a key role in driving airway remodelling in severe asthma’, EpiCentral. Available at: https://global.epicentralmed.com/epifundamentals/airway-epithelium-plays-key-role-driving-airway-remodelling-severe-asthma
- Grainge, C.L. et al. (2011) ‘Effect of Bronchoconstriction on Airway Remodeling in Asthma’, The New England Journal of Medicine, 364(20), pp. 2006-2015. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1014350. Available at: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1014350
- Hough, K.P. et al. (2020) ‘Airway Remodeling in Asthma’, Frontiers in Medicine, 7, article 191. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00191. Available at: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2020.00191/full
- Varrichi, G. et al. (2024) ‘Airway remodelling in asthma and the epithelium: on the edge of a new era’, European Respiratory Journal, 63:2301619. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11024394/
- Zhou, Y., Duan, Q., & Yang, D. (2023). In vitro human cell-based models to study airway remodeling in asthma. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 159, 114218. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114218





 1800 278 462
1800 278 462